In this blog, you will learn Prepositions of Time,Pleace & Movement with example sentences.
Definition of Preposition:
The preposition is one of the important parts of speech in grammar. It is used to indicate how a noun or pronoun in a sentence is related to another word. In a sentence, a preposition must always be followed by a noun or pronoun.
Let’s learn the various kinds of Prepositions in English:

Types of Prepositions:
- Simple Preposition
- Double Preposition
- Compound Preposition
- Phrase Preposition
- Disguised Preposition
- Detached Preposition
Simple Preposition:
These prepositions are used to express a relationship between nouns or pronouns. Besides they can also be used to link sentences and clauses together. These Prepositions are one-word prepositions. Single Prepositions are another name for them.
Simple Prepositions Examples:
- Rohit is sitting in the drawing room.
- I kept the workbook on the table.
Double Preposition:
A double preposition is a single word comprised of two simple prepositions. It’s for this reason that they’re known as Double Prepositions.
Double Prepositions Examples:
- Rohit and Reena are sitting inside the class.
- I was hoping you could finish this assignment within one hour.
Compound Preposition:
Prepositions that are formed by adding a prefix to nouns, adjectives, or adverbs are known as compound prepositions.
Compound Prepositions Examples:
- Rohit is standing behind the wall.
- Divide the chocolates between Rohit and Reena.
Phrasal Preposition:
Phrasal prepositions are words or phrases that connect a sentence’s noun or pronoun to the rest of the sentence. These clusters of words represent a single notion. These prepositions generally start with a preposition and end with a preposition.
Phrasal Prepositions Examples:
- Put this assignment in place of that.
- In spite of his hard labor he failed.
Disguised preposition:
These prepositions are not directly used in the sentence but in a shorter form and disguised form.
Disguised prepositions Examples:
- The clock strikes 12 o’clock. (means of + clock)
- I sold my old dress for a dollar. (means per dollar)
Detached Preposition:
Generally, the preposition is followed by a noun or a pronoun. However, detached prepositions are used when the object of the preposition is an interrogative and relative pronoun. In that case, the sentence ends with the preposition. Consider the following examples:
Detached Prepositions Examples:
Which house do you live in?
Where do you come from?
Prepositions of Time
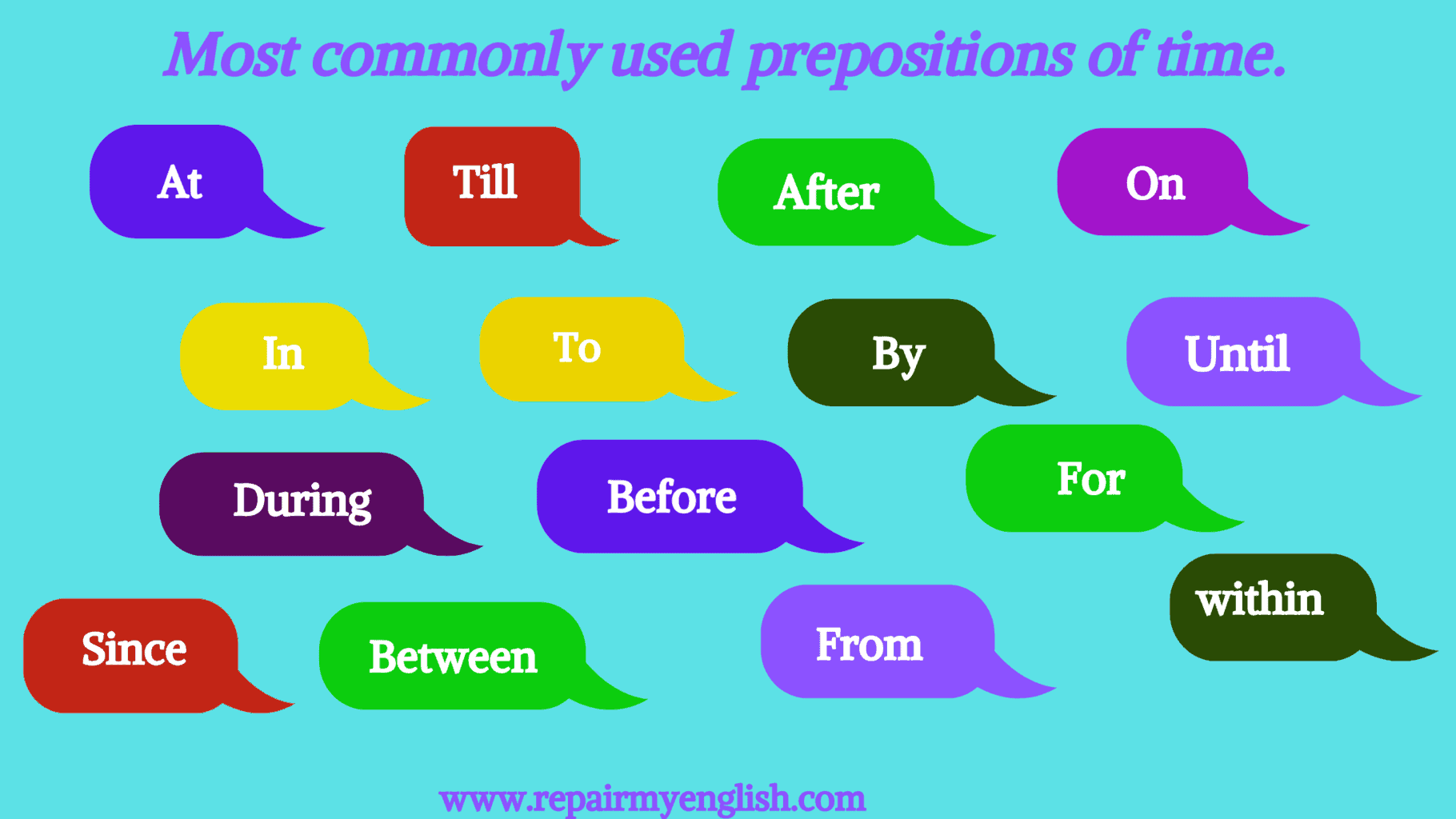
At, On, In, By, during, for, since, from, to, till, until, before, after, between, within
At, On, and In are the most commonly used prepositions of time.
Prepositions of Time Examples:
“At” denotes a specific time:
- Our flight will arrive at 10:00 o’clock.
- I will meet you at 3:30 pm.
“At” denotes the part of the day:
- We reached home at dawn.
- You shouldn’t move out of the house at midnight.
“In” is used to denote three specific parts of the day:
- I take lemon tea in the morning.
- I take salad in the afternoon.
- I take the juice in the evening.
The “In” preposition refers to years, months, and the seasons. Besides, it is also used to denote the time in the future.
- My niece was born in 2015.
- I got married in June.
- We go to hill stations in the summer.
- My friend will come to visit me in a few days.
The “On” preposition refers to days and dates and special days or festivals.
- The conference wil be held on Tuesday.
- My grandfather was born on 15th July 1925.
- Her husband gifted her a red teddy bear on Valentine’s Day.
- I have planned a surprise party on Diwali for my family.
“For” preposition denotes period of time:
- I have been waiting for you for 3 hours.
- He has been delivering his presentation for 15 minutes.
- Rohit has been working in this office for seven years.
- We have been looking for a new house for a few days.
“Since” Preposition denotes the point of time:
- I have been waiting for you since 4:30 pm.
- He has been delivering his presentation since 11:00 am.
- Rohit has been working in this office since 2014.
- We have been looking for a new house since Monday.
“By” Preposition refers to completing an action before a specific time. When we say something will occur before a specific time or simultaneously, we employ the preposition by.
- All students must submit their assignments by Monday.
- We will settle in the US by the following year.
- Reena will reach home by 10:00 pm.
- The examination fees must be submitted by 10th August.
The “From” Preposition is
- The workshop will continue from 8 June to 16 June.
- The restaurant is open from 9:00 am to 12 am.
“Until” Preposition is used when something continues to a specific time. But until the preposition changes its meaning “not before” is used in a negative sentence.
- Her daughter learned the Italian language until the age of 20.
- We will be trekking in the forest until Sunday.
- It would be best not to start your presentation until the audience arrives.
- We can’t start the debate competition until the judges arrive.
Note: Till is an alternative preposition
Prepositions of Place: “At, On, In”
At, On, In
- “At” Preposition is used for a place we refer to as a specific point rather than an area.
- “At” Preposition is used to refer to an event.
- “At” is used to refer to an address.
Prepositions of Place Examples:
Examples of At Preposition:
- I met many relatives at Jaya’s birthday party.
- You should meet me at City Station at 9:30 p.m.
- My cousin lives at 40 Malabar Road.
“On”
- “On” is used to refer to the flat surface.
- “On” is used to indicate the place which is near to the river.
Examples of On Preposition:
- Keep all the assignments on the table.
- Haridwar is on the river, Ganga.
“In”
- “In” refers to a position within a larger area.
- “In” refers to a place where someone lives and stays there.
- “In” is used to refer to kind of places like banks, restaurants, and museums, and so on.
Examples of In Preposition:
- There are numerous medicinal plants in the garden.
- My best friend was born in the Netherlands.
- Reena works in a restaurant.
Preposition of Movement:
Prepositions of direction are also called Preposition of movement. It shows where a noun—a person, place, or thing—is in relation to another noun. Verbs of motion frequently have prepositions following them before a noun or pronoun. To convey motion, direction, or purpose, the prepositions to, towards, on, and in are covered in this handout.
Preposition of Direction Examples:
To
- To can be used to convey movement toward a specific location.
- When used as an infinitive with a verb, it conveys purpose as well
Examples of “To” Preposition:
- Dorothy ran to her coaching classes as she got late.
- She went to Café Coffee Day to enjoy the cold coffee.
- We had to stay late in the office because the inspection team arrived late.
- I worked overnight to complete my book chapter.
Towards:
The preposition “towards” denotes movement in a specific direction.
Examples of “Towards” Preposition:
- The rocket was moving towards the hero of the movie in the climax.
- She is heading towards the target to win the game.
Into:
Into preposition denotes an enclosed place or object.
Examples of “Into” Preposition:
- The bus fell into the ditch carrying 50 passengers.
- The student came into the teacher’s cabin without taking permission.
Across:
Across preposition indicates crossing a river, a straight road, or something straight.
- My childhood friend resides just across my street.
- We saw the walls across the road painted in murals.
Along:
We use along to denote movement in a line next to long, narrow objects, such as
- Walking along the seashore is the most calming moment for me.
- Driving along the mountains can be dangerous.
Behind:
Behind preposition denotes being on the opposite side of something, possibly out of sight.
- My friend’s grocery shop is just behind his house.
- We parked the car just behind the café.
Off:
Off preposition denotes down or away, particularly from the present location, time, or position:
- Jack got injured because he jumped off the moving train.
- John fell off the chair because it broke.
Over:
Over preposition is used to describe movement or position that is above something:
- The eagle just flew over the kid’s head while he was playing badminton.
- The students jumped over the fence to bunk their classes.
Through:
Preposition is used from one end to the other or from one side to the other.
- When we lost our way during camping, we had to go through the dense forest to reach the main road.
- When you visit hill stations, you must pass through the various tunnels.
For related topics visit our Grammar Page.