Interjections in English Grammar:
In this blog, you will learn about the interjections that you use frequently in English Grammar.These interjections are one of the important parts of speech.
What are Interjections?
Interjections are one of the parts of speech used in English Grammar. Usually, it is used informally rather than formally. These interjections express emotions like anger, happiness, and surprise, followed by a sign of exclamation. They are frequently used when we greet someone or at the end of a conversation. But these interjections are not grammatically connected to the other parts of the sentence.
Examples of Interjections:
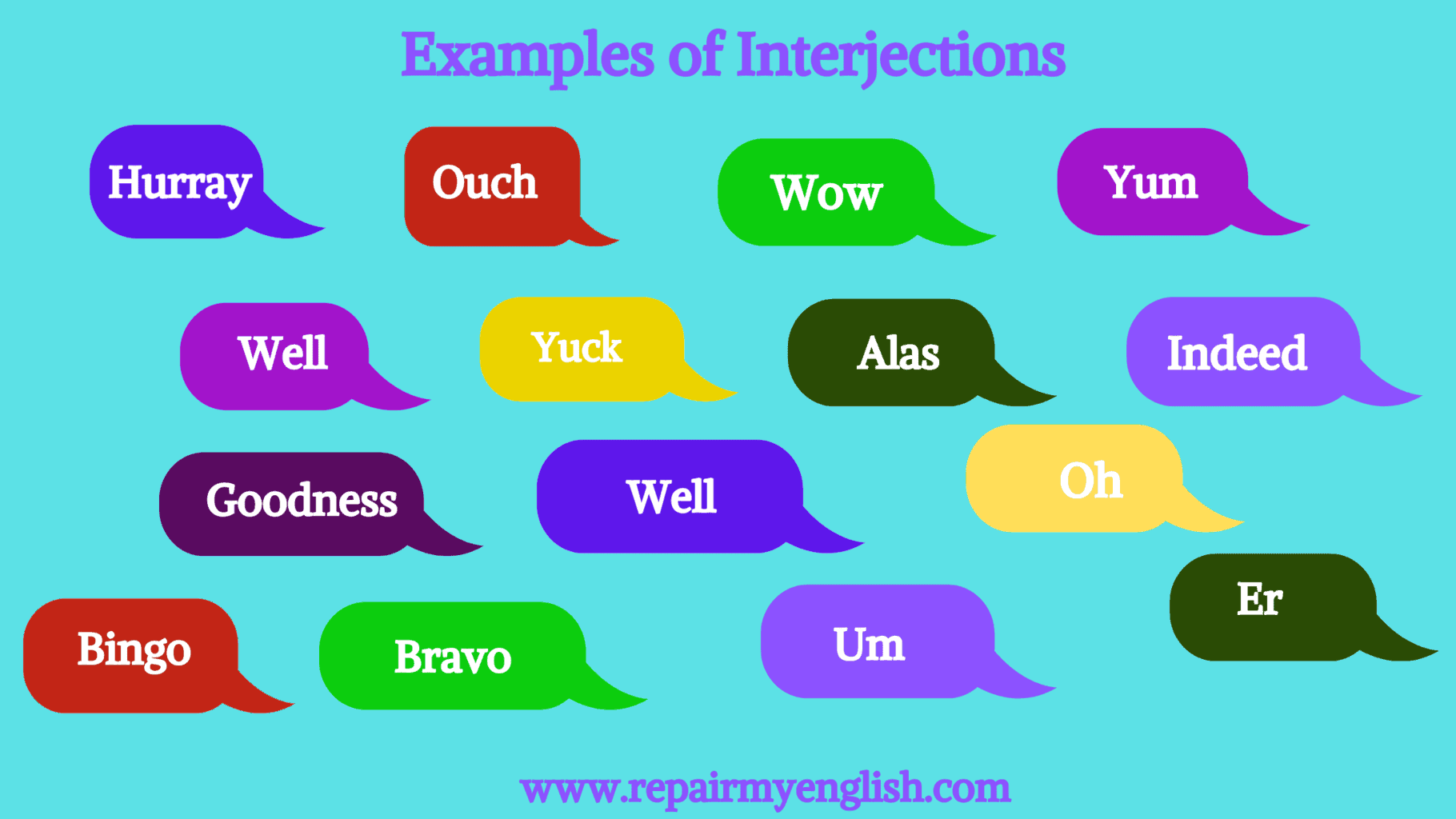
Let us discuss some example sentences of interjections to learn how they can be used in sentences effectively.
- Hurray! I won the prize in the debate competition.
- Ouch! My ankle got twisted.
- Wow! That is a beautiful gift I have ever received.
- Yum! The ice cream is delicious.
- Well! Let me discuss your problem with the boss.
- Yuck! The Oreo shake taste is disgusting.
Let us discuss 10 types of Interjections:
Primary Interjections:
Those words that are only used as interjections in sentences and cannot be classified as any other Parts of Speech are known as primary interjections.
Examples of Primary Interjections:
- Wow! You decided to join us.
- Alas! I was unable to arrive in time.
Secondary Interjections:
Secondary interjections refer to certain types of Parts of Speech, such as Nouns, Adjectives, adverbs, etc., when they occasionally serve as interjections.
Examples of Secondary Interjections:
- Indeed, I did anticipate your initial warning.
- Goodness! How did you read all five of these novels in one day?
Mild Interjections:
Mild Interjections are the terms that are typically used to indicate moderate feelings and emotions. Usually, commas are used to separate these words from the rest of the sentence.
Examples of Mild Interjections:
- Oh, Your friend was looking for you.
- Well, it was effortless.
Strong Interjections:
Strong Interjections are terms that are used to indicate intense emotional outbursts. Exclamation marks are frequently used to separate these interjections from the rest of the sentence.
Examples of Strong Interjections:
- Yay! Finally, I succeeded.
- Bingo! We Located it.
Volitive Interjections:
In the sentence, it is employed to issue a request or an order.
Examples of Volitive Interjections:
- Shh! You are singing, and I cannot concentrate.
- Ahem. Pay attention, please.
Emotive Interjections:
Words can be used to convey an emotion or a response to something.
Examples of Emotive Interjections:
- Ugh! What is that foul odor? (Ugh, intolerable smell)
- Ouch! My ankle got twisted. (It hurts)
Cognitive Interjections:
The terms convey ideas or thinking processes individuals encounter and comprehend through personal experience.
Examples of Cognitive Interjections:
- Gosh! He is so quick.
- Bravo! We finally won the match.
Discourse Marker Interjection:
These interruptions convey the speaker’s mood, mark the beginning or finish of a conversation, or change the subject.
Examples of Discourse Maker Interjection:
- Anyway, leave the matter.
- By the way, have you attended the webinar earlier?
Fillers:
These interjections fill in any gaps in a conversation or express hesitation, confusion, or a lack of words.
Examples:
- Um, I do not remember anything.
- Er, let me see, what can we do?
Parenthetical Interjection:
We use these interjections to add a comment or explanation in the middle of the sentence.
Examples of Parenthetical Interjection:
- She was, I mean, really upset about the situation.
- My brother, well, is not sure about his new job.
- Her mother is, I mean, really upset about her daughter’s wedding.
Rules of Interjections:
Rule 1:
Interjections emphasize a change in mood, emotion, or feelings. Numerous taboo terms are frequently used in casual contexts but avoided in formal situations. These words can be classified as interjections.
Examples:
- What! Are you serious?
- Wow! What a breathtaking scene!
Rule 2:
Interjections occasionally grab someone’s attention for a bit of a while, interrupting a conversation or an idea. They are just sounds that don’t convey any meaning, hence not considered words.
Examples:
- Your clothing, uh, has a stain on the back.
- Um, I’d like t to ask you out on a date.
Rule 3:
Some interjections use the words “yes” or “no.”
Examples:
- Yes! Without a doubt, I will carry it out.
- Nope, we are staying home.
Rule 4:
Some Interjections are used to draw attention.
Examples:
- Yoo-hoo! Is anyone around?
- Hey! Can I take your pen?
Placement of Interjections:
Interjections can be placed in the sentence’s beginning, middle, and end. Let’s discuss this in detail:
Interjectins used in the Beginning of the Sentence:
Interjections at the start of a sentence set the mood for the entire phrase and immediately make the emotion evident.
Interjections used in the Middle of the Sentence:
Interjections that come in the middle of an idea or phrase frequently break it up and emphasize a strong feeling or response.
Interjections used in the End of the Sentence:
Interjections at the end of a phrase can highlight the sentiment or emotion expressed by serving as a punctuation mark.
Skilfully using interjections can produce a more compelling and emotionally charged message.
- Beginning Example: Phew, we made it just in time.
- Middle Example: The cake, ugh, is stale.
- End Example: I can’t believe we finished the project, finally!
For related topics visit our Grammar Page.
For More Topics: